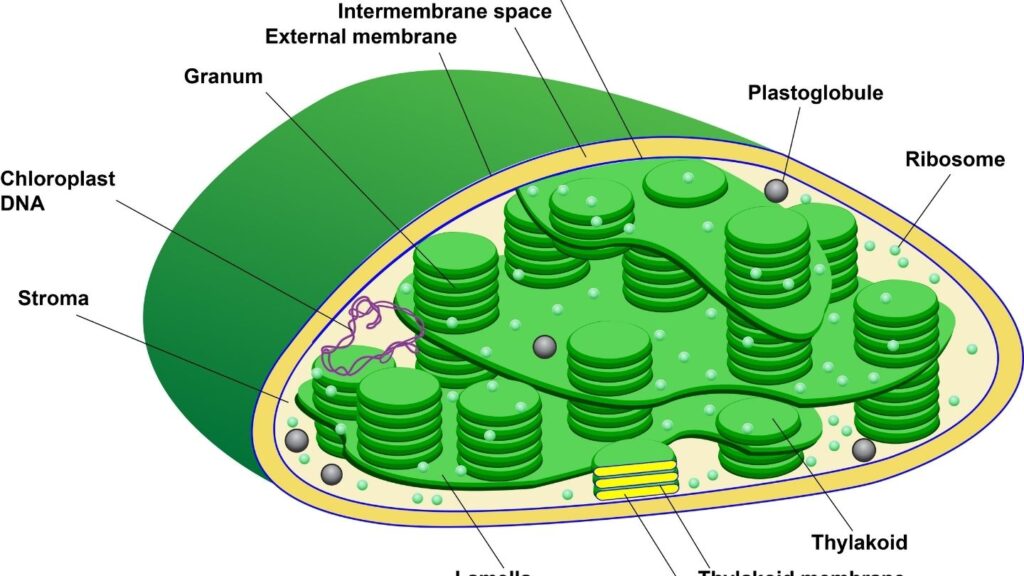
The chloroplast is a structure that contains three membrane systems, the outer, inner, and stroma. Within these structures are grana, which are sacks that store nutrients. Inside a grana, are thylakoids, disk-like structures that harvest photons from the light source. The thylakoids contain proteins and lipid components for the chloroplast membrane. The stroma is where the dark reactions of photosynthesis and the production of sugars occur.
The chloroplast envelope consists of an inner membrane, an outer membrane, and an intermembrane space. Inside the cell, there is a fluid-filled space called the stroma. The stroma also stores energy, which makes it an essential part of the chloroplast. In addition, it helps the plant capture energy from the sun. This process requires photosynthesis to occur. The energy released by photosynthesis is used to build proteins, fatty acids, and membrane lipids. The organelles are also important in protecting plants from pathogens and allowing the plants to grow.
Chlorophyll is a pigment that traps solar energy and converts it into chemical energy. This is the basic mechanism by which plant cells produce food. The photosynthesis process in the chloroplast produces molecular oxygen and NADPH, which are crucial for the metabolism of plant cells. By using light energy, plants produce carbohydrates, starch, and hormones. In addition, chloroplasts act as a barrier against pathogens, which explains why plants do not have specialized immune cells.
The chloroplasts have multiple functions. One of them is to absorb light energy and convert it into chemical energy. This energy is used to synthesize food. This process is known as photosynthesis. Photosynthetic enzymes in the chloroplast bind to the light energy from the sun. The plants also produce ATP and NADPH through the photolysis of water. By absorbing light energy, the photosynthesis process creates the substances needed for life.
The chloroplasts only live in plants, but they also exist in other protists. Their main function is to utilize light energy in the plant’s metabolism. The process is known as photosynthesis, and it is one of the key components in the plant. All green plants contain a chloroplast. This organelle catches sunlight and converts it into sugar. In other words, the chloroplast is vital for the function of the plant.
The chloroplasts are essential for photosynthesis. This process requires light to be absorbed by the plant. The chloroplasts can convert it into oxygen and sugars. The process is called photosynthesis. The light energy reaches the cells in order to make food. The oxygen is used to create the energy. Aside from sugars, other substances are needed in plants for the cell to sustain themselves. For instance, the cell’s cellular chemistry depends on the presence of mitochondrion, which evolved from bacteria.
The chloroplast is a cell that contains DNA and reproduces independently of the mitochondrial and nuclear DNA. It is usually circular in shape and between 120-200 kb in size. The chloroplasts are required for photosynthesis to occur. This process turns sunlight into food, which is why the plant has an ER. This is a crucial function for any plant. The cells in the stroma also produce sugars.
The chloroplasts also perform the important role of photosynthesis. By absorbing light energy and converting it into chemical energy, it allows plants to produce food. They produce oxygen and glucose by using the light energy from the sun. In return, the chloroplasts create NADPH and ATP. The carbon dioxide and oxygen are then used to generate the carbon and sugars needed by the plant. The photosynthesis process in plants involves two processes, a reaction between sunlight and water.
The chloroplasts are the organelles that absorb light energy. In addition, the organelles produce lipids and proteins. A chloroplast diagram shows the different parts of the chloroplast. The outer membrane is the external surface of the chloroplast and the inner membrane is located under it. The intermembrane space is 10-20 nanometers wide. The outer membrane is the external layer of the chloroplast while the inner membrane lies under it.
